숙명여대 학점교류로 듣는 자료구조
day 6. 2021.12.29. 수요일
Search
Sequential search
binary search
interpolation search
hashing search
Sequential search
a search key is searched sequentially from the first item of a list with unordered items
average # of comparisons : (n+1)/2
def seqsearch(num, item, n):
for i in range(n):
if item == num[i]:
return i
return -1레코드에서 아무런 가공을 하지 않고 탐색을 시작한다.
계속 반복적으로 + 순서대로 비교한다.
best case : 1
avg : n / 2
worst : n
O(n)
다양한 방식으로 구현할 수 있다.
binary search
key values are already sorted in ascending order
list[0].key <= list[1].key <= , ... , <= list[n-1].key
mid = (n-1+0)/2
compare searchkey with list[mid].key
until search range becomes 0
problem) search a specified key in a sorted list
* S = [3,7,8,11,13,19,25]
* no overlapping numbers
def binary_search(lst, item, left, right):
while left <= right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if item == lst[mid]:
return mid
else:
if item == lst[mid]:
return mid
else:
left = mid + 1
return -1
mylist = [5,8,91,111]
for item in [60,9,10]:
pos = binary_search(mylist, item, 0, len(mylist)-1)
print("position of %2d = %2d" % (item, pos))
time complexity : O(log2N)
binary search는 범위를 절반씩 쪼개나간다. 후보가 1/2씩 적어진다.
비교 대상이 n개.
그 다음에는 k번을 비교하는데.. 비교하는 대상의 수가 n/2^0, n/2^1, n/2^2, ..., n/2^k-1
레벨의 수가 logn이 나온다.
interpolation search 보간 탐색
자료구조 책에 잘 나오지 않는다.
for a sorted list, this method assumes that key value difference if proportional to key index difference
binary search와는 다르게, it determines the position to compare based on key value difference from a boundary value
(list[right] - list[left]) : (key - list[left]) = (right - left) : (pos - left)
(value) A:B=C:D
a: 전체 양끝의 차이 b : 현재 찾고자 하는 범위 양쪽 값의 차이 c : right - left d : pos - left
이러한 비율을 고려해서 사용한다.
값이 몰려있다면? 10을 찾는 거라면, 무조건 가운데보다는 가까운 쪽(작은 쪽)에서 찾는 것이 좋다.
찾고자하는 수가 비교 대상의 양쪽 경계와 비교했을 때 경계쪽으로 이동해서 찾는다.
찾고자하는 값의 차이가 키 값의 차이와 유사할 것이다.
가변적으로 조정하자!

pos를 찾아보자. 계속해서 left, right 등을 이용해서 값을 업데이트해준다.
binary 는 3번, interpolation은 2번에 탐색할 수 있게 된다.
value, index 이용해서 효과적으로 탐색할 수 있다.
def interpolate_search(num, key, left, right):
while left <= right:
if key < num[left] or key > num[right]:
break
# 유일하게 다른 부분 :)
pos = left + (key - num[left]) * (right-left)// (num[right]-num[left])
if key > num[pos]:
left = pos + 1
elif key < num[pos]:
right = pos - 1
else:
return pos
return -1
lst = [2,3,5,7,8,10,13,20,25,39,45,55]
for key in [39,2,55,60,1]:
pos = interpolate_search(lst, key, 0, len(lst)-1)
print("%2d is in %2d" % (key, pos))
hashing search
Intro
* conventional search
repeatedly compare a search keywith keys stored
* Hashing search
find a hash table address for a search key by a hash function
hashing : to convert/map a key into a hash table address
* Application
Dictionary : word and meaning
대표적인 사전 - 단어와 뜻이 있다.
* Dictionary
a symbol table with entries (표제어, 명칭)
Entry (key, value) // word, definition
키와 값의 쌍을 엔트리라고 한다.
* applications
word / thesaurus references
spelling checker in word processor or editor
electronic signature encoding / decoding
없는 글자라면, 빨간줄 등록 - 신기하다 ㅎㅎ
지문이 등록되어있는가 / 아닌가
* operations
determine if a particular symbol key exists in the table
retrieve the attributes of a key
modify the attributes of a key
insert a new entry with a key and value
delete an entry
time complexity by hashing search : O(1)
static hashing

Dynamic hashing
ex) 동적 해싱 80~90%가 차 있다면, 2배로 늘리기
- reconfigure that hash table size flexibly according to the frequency of key collision
주소로 변환해준다(hash table에 여러 bucket 주소)
identifier가 hash table로 들어갈 수 있다.
모든 명칭을 hash table에 다 넣은 수는 없다.
다 넣기보다는, 검색 빈도가 높은 부분만 미리 넣어둔다(Cache처럼)
Hash Table
keys are stored in a fixed size table, called a hash table
* row : buckets [0, b-1]
* col : slots [0, s-1]
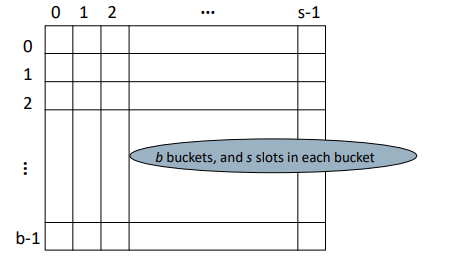
Hash Table
Def) Identifier density of a hash table 명칭 밀도
전체 identifier 중에 얼마 만큼이 hash table에 저장되어있는가
ID = n/T
( n = # of identifier in tabel)
( t = total # of identifier)
Def) Loading density(or factor) of a hash table
LD = n/N
(N = s * b)
( s = # of slots in each bucket)
( b = # of buckets)
Def) Synonym 동의어
Two identifiers i1 and i2 are synonyms with respect to f(x)
if f(i1) == f(i2) where i1 != i2
명칭이 서로 다르지만, 해시값은 동일하다. (home bucket이 같은 것)
Def) Overflow
어떤 명칭 identifier i가 full bucket에 할당되었을 때 발생함
Def) Collision 충돌
collision occurs when two non-identical identifiers are mapped into the same bucket
collisions and overflows occur simultaneously if the bucket size is 1
동일하지 않은 identifier가 하나의 bucket으로 할당됨
Hash Function
build a hash table (b = 26, s = 2) with the following identifier by a hash function f(x) that returns 1st character of identifier
{acos, define, float, exp, char, atan, ceil, floor, clock, ctime}
| Bucket | Slot 0 | Slot 1 |
| a(0) | acis | atab |
| b | ||
| c | char | ceil (clock, ctime overflow) |
overflow랑 collision이 어떻게 다른 건지 잘 모르겠다.
Hash Function
Requirements of the hash function* easy to compute* minimize the number of collisions
명칭의 분포에 따라 적절히 hash 함수를 정의하여야 한다.
Uniform hash function
for a randomly chosen x from identifier space,
p[f(x) = i]=1/b for all buckets i
a random x has an equal chance that is hashed into one of b buckets
ex) f(x) = x%10 where b is 10
=> 이상적인 것
해시 함수는 어떻게 정의하지?
Examples
- Mid-Square
frequently used in symbol table applications
Fm(x) = r bits of x^2
square the identifiers : 1010 ^ 2
=> 편중 분포를 줄이기 위한 목적
obtain the bucket address by extracting an appropiate number of bits
r bits are needed for 2^r buckets
=> 1010^2 = 1100100 => 2^3 = 8 buckets
- Division ( modulo 연산 )
use the remainder operator (%) for hashing
Fd(x) = x % D
if D == b where table size if b, f(x) is uniform hash function
if D is divisible by two => can be biased (2는 지양할 것)
odd numbers => odd buckets; even => even buckets
ex) {2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20} % 8 => even bucket
choose D as a prime number
- folding
fold a key value by r digits, depending on hash table size
identifier x = 12320324111220
1. shift folding
x1 = 123
x2 = 203
x3 = 241
x4 = 112
x5 = 20
h(x) = 699
2. boundary folding
짝수번째 아이를 수를 뒤집어서 정한다.
- Digit Analysis 숫자 분석 조사법
useful when all the keys are known in advance
delete those digits that had a skewed distribution
ex) 200512345 : 중복되는 부분이 많다(2005).
Because the first 4 digits stand for a year and can be skewed, remove it
the last 5 digits are appropriate for a hash address
class Hashing:
def __init__(self, size, hf):
self.size = size
self.table = [None] * size
self.collision = []
def hf(self, key):
total = 0
for s in key:
total += ord(s)
return total % self.size
def add_table(self, sym):
bucket = self.hf(sym)
if self.table[bucket] is None:
self.table[bucket] = sym
else:
self.collision.append(sym)
def show_table(self):
i = 0
for item in self.table:
print("%2d" %i, item)
i += 1
symbol = ['for', 'while', 'if', 'else', 'elif', 'def', 'class', 'self', 'return', 'range', 'list', 'tuple', 'ceil']
h = Hashing(26,1)
print("Symbols = ", len(symbol))
for item in symbol:
h.add_table(item)
h.show_table()
print("Hash function = ", h.hf)
print("collision = ", h.collision)
print("Collisions = ", len(h.collision))
'Computer Science > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 자료구조 | Singly Linked List | Linked List (0) | 2021.12.29 |
|---|---|
| 자료구조 | Maze Problem | linear DS (0) | 2021.12.29 |
| 자료구조 6강-2 | Linked List | 숙명여대 학점교류 (0) | 2021.12.29 |
| 자료구조 | 수식 변환 계산 expression evaluation | postfix, prefix (0) | 2021.12.28 |
| 자료구조 6장 | Linked List | 숙명여대 학점교류 (0) | 2021.12.27 |