학점교류로 수강하는 숙명여대 자료구조 계절학기 수업
Performance Analysis
성능 분석이 무엇인가?
공간 복잡도, 시간 복잡도, 점근적 표기법
- ideal criteria 정성적 분석어느 정도의 성능을 발휘하는지 보아야 한다. Does a program meet the original requirement of the task? Does it work properly?Does it effectively use functions to perform a task?
- realistic criteria 정량적 분석space complexity : the amount of memory space that a program needs to complete the executionㄴ 파이썬에서는 어떻게 해야하는거지?time complexity : the amount of computational time for execution
Space Complexity
- fixed space requirements
memory space for
instructions, variable, fixed-size structured variable, constants
- variable space requirement -> 주요 관심사
실행 중에 달라지는 부분 : array passing, recursion
- total space complexity
S = Sc + Sv
example) simple variables
def abc(a, b, c):
return a+b*c+(a+b-c)/(a+b)+4.00이 함수에서 variable space requirements는Sv(abc) == 0
space complexity
def iSum(num):
total = 0
for item in num:
total = total + item
return totalinput : an array and an integeroutput : a simple float variableㄴ space complexity depends on array passing method
call by value, call by reference
파이썬에서의 call by reference는?
call by value
array elements are copied to function
additional memory space is required in proportional to array size
ex) pascal
call by reference -> date 2에서 나오는 내용..
the base address of array is passed to function
no additional memory space required : Sv(sum) = 0
ex) C, python (only for mutable data type as list)
sum - recursion
at each function call, the followings must be saved
variables : num
return address
n times function calls : rsum(n-1) ... rsum(0)
space complexity = n*size(num) # num = local variable
def rsum(num):
if len(num):
return rsum(num[:-1])+num[-1]
else: return 0
print(rsum[1,2,3,4,5])
Time Complexity
Time complexity T의 경우는?
amount of time taken by an algorithm to complete a task
T = compile time(Tc) + execution time(Te) (주요 관심사)
execution time depends on computing environment
counting instruction steps is more objective, and less accurate though
환경마다 가변적인 물리적인 시간 (00:00초)를 재는 것보다
논리적인 실행해야 할 명령어 수를 계산하는 것이 더 의미있다. (== instruction steps)
명령어마다 다르다는 점은 무시한다.
Step count table (명령어 개수를 가지고 계산하는 방식)
steps
instructions per line 한 라인에 명령어가 몇 개 있는가
frequency
the number of execution times for each instruction
for, while etc
total steps
steps * frequency per line
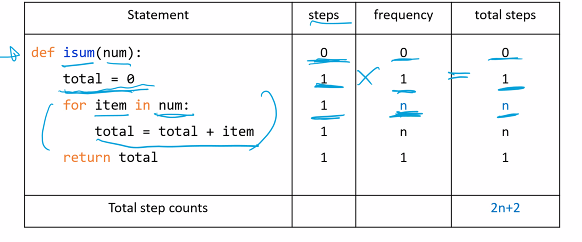
ex1) Step count table(iterative sum)
step 1. count steps
각 line마다 몇 개의 명령어를 수행하는가?
step 2. frequency
각 명령어는 몇 번 수행되는가?
step 3. total steps
line마다 count * frequency를 곱해서 계산한다.
그리하여 n이 중요함
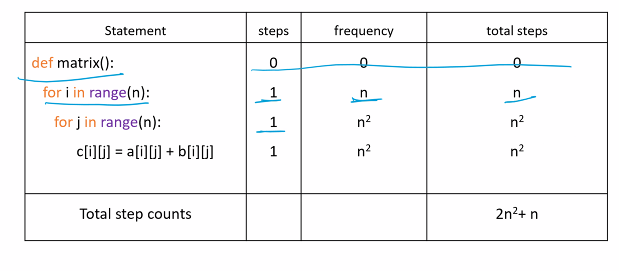
ex1) step count table(matrix addition)
step 1. count steps
각 line마다 몇 개의 명령어를 수행하는가?
step 2. frequency
각 명령어는 몇 번 수행되는가?
step 3. total steps
line마다 count * frequency를 곱해서 계산한다.
결국 이 예제는 n^2이 중요하다.
ex1) step count table (recursive sum)
step 1. count steps
각 line마다 몇 개의 명령어를 수행하는가?
step 2. frequency
각 명령어는 몇 번 수행되는가?
step 3. total steps
line마다 count * frequency를 곱해서 계산한다.
이 예제는 n부터 0까지 수행되니까 n+1 어쩌구
if num: 이하 문장은 n번 실행된다. (0은 거짓이기 때문)
재귀 호출은 frequency 유의해야 한다.

Asymptotic Notation
Big(O) notation
- time complexity
T = n^2 + 2n => O(n^2)
input : n
n이 증가하면서, 항이 2항(1차항, 2차항)이 있다.
어느 항이 빨리 증가하는가? => 2차항
따라서 n^2만을 표기한다.
to approximate a time complexity asymptotically where n is very large
implies how much time an algorithm consume to run if n increases
a standard for evaluating the algorithm performance : 이를 통해 알고리즘을 비교할 수 있게 된다.
example ) n^2+2n vs 100n
어떤 알고리즘을 채택하는 것이 좋을까?
n^2 + 2n == 100 n
n + 2 = 100
만약 n<=98이라면, f1 = n^2 + 2n이 더 효율적이다.
이보다 n이 크다면, f2가 효율적이다.
if n=100000, then 100000^2 + 100000 > 100000
as n increases
T1 takes much more time than T2
we should choose T2
the smaller, the better
Asymptotically notated in Big Oh
T1 = n^2 + 2n => O(n^2)
T2 = 100n => O(n)
Big(O) notation
- def)
f(n) is in O(g(n)) iff
there exist positive constants c and n0 that satisfy f(n) <= c*g(n) for all n>= n0
c, n0가 있어야 한다. (n0는 n의 시작점, c는 fn의 상한선을 규정)
c*g(n) is upper bound of f(n)
f(n) takes less time than c*g(n)
ex) prove f(n) = 10n + 10000 is in O(n)
choose c and n0 with 20 and 1000
f(n) is in O(n) as f(n) <= 20n for all n>= 1000
즉, 1000이상의 구간에 대하여 항상 O(n) (20n)이
f(n)보다 크다.
ex) prove f(n) = n^3 + n^2 + n is in O(n^3)
choose c and n0 with 3 and 1
f(n) is in O(n^3) as f(n) <= 3n^3 for all n>= 1
무조건 n0와 c가 있어야 한다는 것임
이후의 모든 구간에 대해서 항상 그 위에 있다고 표기한다.
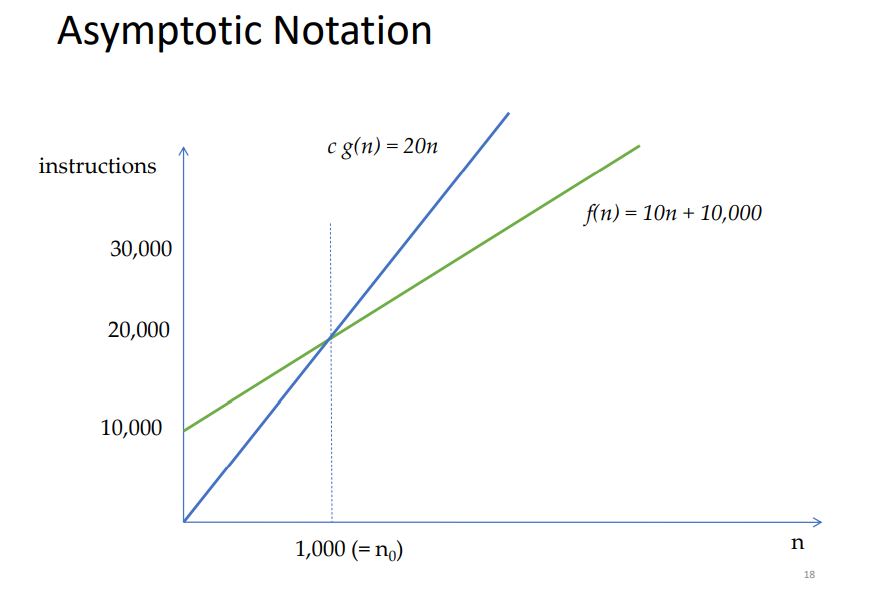
why f(n) <= cg(n)
because g(n) grows faster than each term of f(n),
c times g(n) increases always faster than f(n)
choose c by considering the coefficient of a dominant term and number of terms of f(n)
ex)
f(n) = n^2 + n <= 2n^2 = O(n^2)
c = 2
n0 = 1
f(n) = 2n^2 + n <= 3n^2 = O(n^2)
c = 3
n0 = 1
big oh notation
ex)
- 3n + 2 is in O(n)
3n + 2 <= 3n + 2n <= 5n for all n>= 2
n0 = 2
c = 2
- 10n^2 + 4n + 2 is on O(n^2)
10n^2 + 4n + 2 <= 11n^2 for n >= 5
n0 = 5, c = 11
- 6*2^n + n^2 is in O(2^n)
n0 = 4, c = 7
- 3n+3 is in O(n^2)
n0 = 2
c = 3
(사실 더 가까운 것은 O(n))
- log n + n + 3 is in O(n)
n0 = 1
c = 4
- nlogn + n is in O(nlogn)
n0 = 3
c = 2
- 3n+2 is not in O(1)
- 10n^2 + 4n + 2 is not in O(n)
c와 n0이 존재하지 않기 때문이다.
Big Omega Notation
Big Theta Notation
Practical Complexity
ex) 1bps computer (=1 billion inst./sec (10^9/sec))if a program runs an algorithm
'Computer Science > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 자료구조 4강 | Recursion | 숙명여대 학점교류 (0) | 2021.12.24 |
|---|---|
| 자료구조 2-1강 | Array and List | 숙명여대 학점교류 (0) | 2021.12.23 |
| 자료구조 1-1강 | Introduction | 숙명여대 학점교류 (0) | 2021.12.22 |
| 자료구조 0강 | 강의 소개, 일정, 평가 등 | 숙명여대 학점교류 (0) | 2021.12.22 |
| singly linked list (0) | 2021.11.06 |