학점교류로 듣는 숙명여대 자료구조
day 2. 2021.12.23. 목
day 3. 2021.12.24. 금
Recursion
Introduction
Factorial
GCD
Binary Search
Fibonacci Numbers
Hanoi Tower
Permutation
N Queens Problem
Recursion Introduction
a function is called by itself while running
"divide & conquer" strategy
possible when the same task is repeated with exit condition
Iterative function with if-else or while can be rewritten in recursion
in compiler's view, recursive call is the same as another new function is called
Adv) concise representation of algorithm
Disadv) Frequent function call overhead
Factorial
n! = 1 where n=0
n! = n*(n-1)! where n>= 1
반복문보다 편할 때가 많음 (정확하다면..)
def fact_r(n):
if n==0: return 1
else: return fact_r(n-1)*n
i=20
for n in range(1, i+1):
print(n, '!=', fact_r(n))
GCD
Greatest Common Divisor
gcd(x, y) = gcd(y, x%y) if y >0
gcd(x,0) = x
def gcd(x, y):
if y==0: return x
else: return gcd(y, x%y)
num = [(128,12), (45,120)]
for x, y in num:
print("gcd(%d,%d)=%d" % (x,y,gcd(x,y)))
Binary Search
problem) search a specified key in a sorted list ( 정렬된 리스트를 탐색할 때 사용 가능)
S = [3,7,8,11,13,19,25]
no overlapping number
algorithm
원하는 것을 찾을 때까지 탐색하는 : 순차 탐색
이진 탐색
while (there are any item to compare):
find the median position
if (item < median)
change the search range with left sub-list
else if (item > median)
change .. with right sub-list
else:
return item.index
pseudo code
def rbinsearch(lst, item, left, right):
if left <= right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if item == lst[mid]:
return mid
elif item < lst[mid]:
return rbinsearch(lst, item, left, mid-1)
else:
return rbinsearch(lst, item, mid+1, right)
mylist = [5,8,9,11,13,17,23,32,45,52,60,72]
print(mylist)
for item in [60,9,10]:
pos = rbinsearch(mylist,item,0,len(mylist)-1)
print("position of", item, " = ", pos)범위를 바꾸어서 recursive하게 이진 탐색을 한다.
리스트에 없는 요소의 경우, left가 더 커지는 경우가 못 찾은 경우
return -1이 된다.
Fibonacci Numbers
import time
def fibo1(n):
global count1
count1 += 1
if n <= 1:
return n
else:
return fibo1(n-2)+fibo1(n-1)
for num in [10,20,30,40]:
count1 = 0
time1 = time.time()
print("fibo1", num, "=", fibo1(num))
time2 = time.time()
print("time1 = ", time2-time1)
print("recursion1 = ", count1)fb가 여러 번 중복되어 호출되게 된다.
더 효율적인 방법은 없을까?
def fibo2(n):
global count2
count2 += 1
if n<=1:
return (0,n)
else:
(a,b) = fibo2(n-1)
return (b,a+b) # 직전 수랑 같이 보내준다
# 중복 호출을 피할 수 있다
# 이러면, 10을 구하라고 했을 때 재귀 호출이 10번만 일어난다.
# 9, 8, 7, 6.. 을 호출
for num in [10,20,30,40]:
count2 = 0
time1 = time.time()
print("fibo2", num, "=", fibo2(num))
time2 = time.time()
print("time2 =", time2-time1)
print("recursion2 = ", count2)
print(fibo2(10))
Hanoi Tower
goal of Problem
move some discs in an initial pole to a target pole without changing the disc order
condition
only single disc can be moved at a time
any disc cannot be placed over smaller one
algorithm (recursive)
assuming that there are three poles A, B, C,
and all discs of pole A have to be moved to pole B : htower(n)
- Move n-1 discs from pole A to pole C : htower(n-1)
- Move single disc from pole A to pole B : A->B
- Move n-1 discs from C to pole B : htower(n-1)
step 1 and 3 should be solved recursively
원반 하나만 남으면, 종결 조건
def htower(n, a, b):
global count
count += 1
if n==1:
print("Disc %d, moved from Pole (%d) to (%d)" % (n,a,b))
else:
c = 6-a-b # 1 + 2 + 3 = 6 # 비어있는 기둥
htower(n-1,a,c)
print("Disc %d, moved from Pole (%d) to (%d)" % (n,a,b))
htower(n-1, c, b)
count = 0
n = int(input("Enter disc number:"))
htower(n, 1, 2)
print("# move for %d discs : %d" % (n, count))
calculate # of disc movements
time to move single disc
- t(1) = 1
time to move n discs
- t(n) = 2t(n-1) + 1
= 2(2t(n-2)+1) +1
= ...
= 2^n - 1
t(n) = O(2^n) // Time complexity
매우 비효율적임..
Permutation
find all possible permutations with n elements(n>1)
ex) for a set {a,b,c}, find all permutations
P = {(a,b,c), (a,c,b),(b,a,c),(b,c,a),(c,b,a), ()}
permuatations of {a,b,c,d}
24 permutations are divided into 4 groupts
perm(b,c,d) can b solved in the same way
a) (a, perm(b,c,d))
b) (b,perm(a,c,d))
c) (c,perm(a,b,d))
d) (d,perm(a,b,c))
원소가 하나일 때 -> 종결 조건
def permutation(word, i, n):
if i==n: print(word)
else:
for j in range(i, n+1):
# L로 시작하는 그룹
# A로 시작하는 그룹
# N으로 시작하는 그룹
# G로 시작하는 그룹
word[i], word[j] = word[j], word[i]
permutation(word, i+1, n)
word[i], word[j] = word[j], word[i]
word = ['L', 'A', 'N', 'G']
permutation(word, 0,3)
N Queens Problem
problem : how to place N queens on an N*N chess Board such that no queens may attack each other
Fact : queens can attack at any distance vertically, horizontally, or diagonally
observation : different queen in each row and each column
가장 강력한 말..
이 문제는 n*n 체스판에서 n개의 queen을 놓으려고 하는데,
서로 잡아먹지 않도록 배치한다.
8 queens problem - solution
8*8 board에 8개의 queen을 놓는다.
전체 경우의 수는
[조합으로 보았을 때]
64C8 = 4426165368으로 매우 큼
[순열로 보았을 때]
row 8개
col 8개
각각 하나씩 놓아야 한다.
이런 관점으로 보면? 칼럼의 순서를 어떻게 정할 것인가.
8! = 40320
Backtracking algorithm
모든 경우의 수를 트래킹하면서,
그 밑의 경우는 탐색하지 않고 다음 경우로 넘어가는 방법
backtracking - 4 Queens
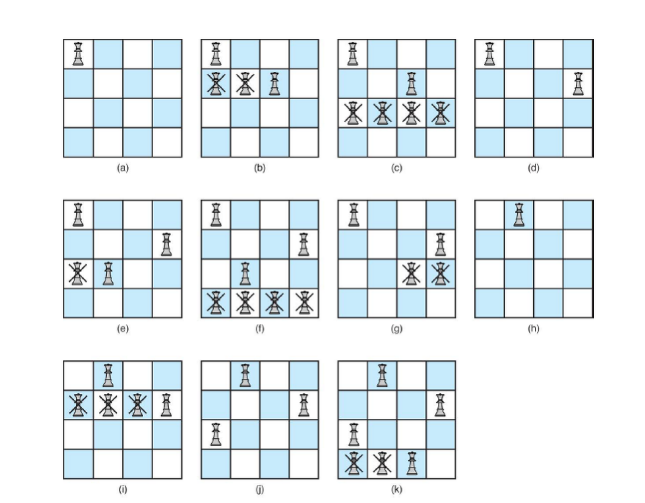
마지막행에 놓을 것을 찾을 수 없다.
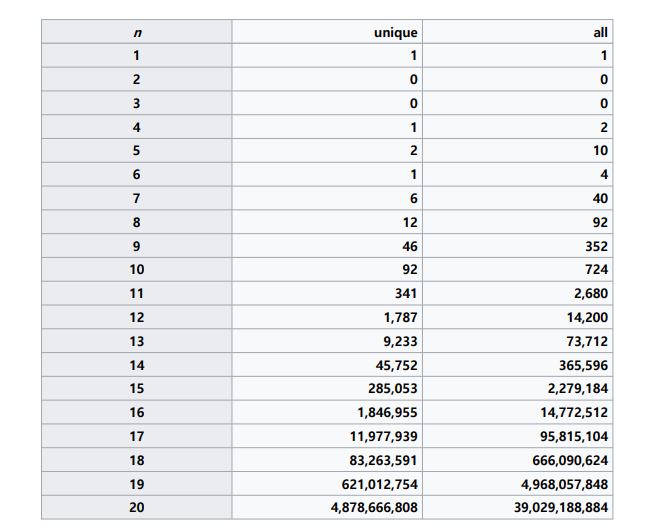
solutions
대칭인 해는 하나만 추적
class NQeens:
def __init__(self, size): # 순열 문제와 같다.
self.size = size
self.solutions = 0
self.col = [-1] * size
def put_queen(self, row):
if row==self.size:
self.show_board()
self.solutions += 1
else:
for col in range(self.size):
if self.check_pos(row, col):
self.col[row] = col
# queen을 놓음
self.put_queen(row+1)
def check_pos(self, rows, col):
# 잡아먹는 queen이 있는지 check
for i in range(rows):
if self.col[i] == col or \
self.col[i] - i == col - rows or \
self.col[i] + i ==col + rows:
return False
return True
def show_board(self):
for row in range(self.size):
line = ""
for column in range(self.size):
if self.col[row] == column:
line += 'Q'
else:
line += "+ "
print(line)
print()
N = 4
q = NQeens(N)
q.put_queen(0)
print(q.solutions, "solutions found")
'Computer Science > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Simple Data Structure | Queue, Circular Queue, Stack, N Queens Problem, fraction, prime number, fibonacci, bowling game, binary search (0) | 2021.12.25 |
|---|---|
| 자료구조 5장 | Linear Data Structure | 숙명여대 학점교류 (0) | 2021.12.25 |
| 자료구조 2-1강 | Array and List | 숙명여대 학점교류 (0) | 2021.12.23 |
| 자료구조 1-2강 | Algorithm Analysis | 숙명여대 학점교류 (0) | 2021.12.22 |
| 자료구조 1-1강 | Introduction | 숙명여대 학점교류 (0) | 2021.12.22 |